
Monthly Archives: August 2015
It’s About the Bread

Those who have been reading this blog for any length of time are at least peripherally aware of the eschatology espoused here. We believe that the prophesied Antichrist of which we are warned by the apostles and prophets was manifested in the rise of Roman Catholicism and is personified in the Papacy of Rome. As we noted last week, in The Fourteenth Diocese, Daniel foresaw that the Antichrist would emerge among of the thirteen fragments of the Roman Empire, would uproot three dioceses in the process, subduing their three metropolitans, and rise up among the remaining ten, growing “more stout than his fellows” (Daniel 7:8,20-22,24-26). That is precisely what Roman Catholicism did as it claimed Rome, Alexandria and Antioch as a single See of St. Peter, aggregating for itself the three Dioceses of Italy, Egypt and Oriens. The papacy of Rome is the Little Horn of Daniel 7 and the dioceses of Diocletian’s reorganization are the other horns of the vision. That reorganization into dioceses began in 293 A.D., and was completed by the end of the fourth century. As prophesied, Roman Catholicism emerged during that time frame when the Papacy came up among the dioceses, “speaking great things” (Daniel 7:8).
Continue reading It’s About the Bread
The Fourteenth Diocese
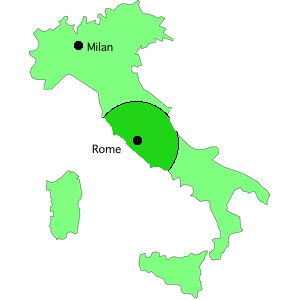
The city of Rome was the capital seat of the empire at its founding, and retained that primacy for centuries. But for a brief period from 293 A.D. to the latter part of the fourth century, Rome was relegated to the status of a third tier Metropolis behind the tetrarch capitals and the metropolitan seats of Diocletian’s new dioceses. The division of the empire started in 293 A.D. with the formation of 12 dioceses under four tetrarchs, presiding from Nicomedia, Smirmium, Milan and Trier. Each tetrarch was assigned the rule over three dioceses, and each diocese was in turn ruled from its chief metropolis by a vicarius or equivalent. Notably, the city of Rome was reduced in stature, and was made neither a tetrarch capital, nor even the chief metropolis of the Diocese of Italy. Nevertheless, the city of Rome was also assigned its own vicarius, and he ruled over his limited jurisdiction in the heart of Italy. Over the course of the fourth century, the tetrarchy faded away, but the diocesan system endured. Further reorganizations occurred in which two dioceses were combined into one, and two others were divided into four. The eventual outcome by the end of the fourth century was a fully reorganized Roman empire of thirteen dioceses under thirteen vicars—and within one of those dioceses, a greatly diminished city of Rome, a comparatively small vicariate in an empire of dioceses. Although the Vicar of Rome had not received a diocese to manage, the city of Rome and its suburbs comprised what could almost be called a little diocese of their own. We might even call it “the fourteenth diocese.” That little “fourteenth diocese” had been diminished in Diocletian’s reorganization, but under the administration of a pope, it would one day rise up again to rule the empire. Only three metropolitan cities stood in his way, and he would dispatch them short order.
Continue reading The Fourteenth Diocese
The Object of Her Irrepressible Scorn

In our article last week, Longing for Nicæa, we mentioned that Rome’s relationship with the Early Church manifests in a love-hate dichotomy. She loves to identify with the era in order to allege antiquity, but she hates what she finds there, for it betrays her later origins. Last week we showed how frequently Rome appeals to the Nicæan and ante-Nicæan era to prove the antiquity of her novelties, and how frequently she is rebuffed by the Early Church. This week we show how frequently Rome has to distance herself from the Nicæan and ante-Nicæan church because the Early Church was in fact a different religion from Roman Catholicism.
Continue reading The Object of Her Irrepressible Scorn
Longing for Nicæa

Roman Catholicism, as a religion, is a novelty of the late fourth century, but in order to be taken seriously she must at every opportunity claim Nicæan and ante-Nicæan origins for her novelties. Yet at the same time, there is nothing so foreign to Roman Catholicism as the Nicæan and ante-Nicæan Church. For this reason, while Roman Catholicism constantly attempts to lay claim to apostolicity, she must always at the same time distance herself from the practices and beliefs of the Church of the apostles. It is a love-hate relationship. Rome strives diligently to identify herself with the apostolic era, and then exhausts herself explaining why the Church of that era was so different from Roman Catholicism. What we find as we examine Rome’s vain striving for antiquity and continuity is an uncomfortable truth that lies beneath the surface of all of her posturing, a truth that can never be uttered aloud: She does not know whence she came.
Continue reading Longing for Nicæa
 Follow
Follow